Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Terasaka, Yuta; Iimoto, Takeshi*; Saso, Michitaka*; Fujita, Reiko*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(4), p.203 - 207, 2024/04
, 66(4), p.203 - 207, 2024/04
no abstracts in English
Koide, Kaoru
JAEA-Research 2023-003, 101 Pages, 2023/06
This study developed a geobotanical remote sensing method for estimating high water table areas such as groundwater discharge points using differences in the growth conditions of forest trees induced by moisture supply from groundwater in a humid warm-temperate forest area. A new vegetation index (VI) termed AgbNDVI (Added green band NDVI) was proposed to discriminate the differences. The AgbNDVI proved to be more sensitive to water stress on green vegetation than existing VIs: SAVI and EVI2, and possessed a strong linear correlation with the vegetation fraction. To validate the proposed method, a 23 km study area was selected in the Tono region of Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. The AgbNDVI values were calculated from atmospheric corrected SPOT HRV data. To correctly detect high VI points, the influence factors on tree growth were identified using the AgbNDVI values, DEM and forest type data; the study area was then divided into 555 segments according to combinations of the influence factors: elevation, slope gradient, slope aspect and forest type. Thresholds for detecting high VI points were defined for each segment based on a histogram of AgbNDVI values. By superimposing the high VI points on topographic and geologic maps, most of the high VI points are clearly located on the concave/convex slopes and near the geologic boundaries prone to groundwater runoff. In addition, field investigations support the correctness of the high VI points, because the growth increments and biomass of trees (
study area was selected in the Tono region of Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. The AgbNDVI values were calculated from atmospheric corrected SPOT HRV data. To correctly detect high VI points, the influence factors on tree growth were identified using the AgbNDVI values, DEM and forest type data; the study area was then divided into 555 segments according to combinations of the influence factors: elevation, slope gradient, slope aspect and forest type. Thresholds for detecting high VI points were defined for each segment based on a histogram of AgbNDVI values. By superimposing the high VI points on topographic and geologic maps, most of the high VI points are clearly located on the concave/convex slopes and near the geologic boundaries prone to groundwater runoff. In addition, field investigations support the correctness of the high VI points, because the growth increments and biomass of trees (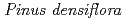 ) are greater than at points other than the high VI points, and they are located around known groundwater seeps and in a high water table area. Consequently, the proposed method can be expected to provide useful information for characterizing hydrogeological structures by combining with conventional photo-geological interpretation.
) are greater than at points other than the high VI points, and they are located around known groundwater seeps and in a high water table area. Consequently, the proposed method can be expected to provide useful information for characterizing hydrogeological structures by combining with conventional photo-geological interpretation.
Takeuchi, Suehiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Yoshida, Tadashi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 513(3), p.429 - 438, 2003/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.69(Instruments & Instrumentation)At the JAERI Tandem accelerator, an acceleration tube replacing plan is proceeding to increase the acceleration voltage toward 20 MV. Lengthy conditioning is generally necessary for a large tube system. We had an idea to clean the tubes with high-pressure water-jet rinsing before installation. We cleaned tubes and tested them at 1 MV and 3 MV. The both results exhibited that the voltages went beyond the rated voltages and discharge activities were much less than the old records. During the test of new tubes at 3 MV, the conditioning proceeded well and an extremely stable condition was fulfilled within 24 hours. In conclusion, the cleaning was found to be a very promising way to improve high-voltage performance of the tubes in a large tube system.
Nagano, Tetsushi; Yanase, Nobuyuki; Tsuzuki, Katsunori; Nagao, Seiya*
Environment International, 28(7), p.649 - 658, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:52.4(Environmental Sciences)In order to investigate the role of suspended particulate matter (SPM) in fluvial discharge of trace and major elements in the Kuji River, Japan, the SPM concentrations in the river water and chemical compositions of SPM were analyzed together with the dissolved form concentrations. The SPM concentrations increased by 2 or 3 orders of magnitude with the water discharge, and also had seasonal variations. The suspended species have the key role in transport of some trace and major elements in some fluvial environments and hence should be taken into account in estimating the total discharge through the river waters.
Matsunaga, Takeshi
JAERI-Review 2001-018, 121 Pages, 2001/06
The present report reviews a series of studies conducted in JAERI which have dealt with the behavior of atmospherically-derived radionuclides in a fluvial environment. The studies cited here firstly include investigations of the evaluation of the transport rate of the atmospherically-derived 137Cs, 210Pb and 7Be from the ground via a river to the downstream areas where the affected water is consumed. The studies validated i) the importance of suspended particulate materials in the fluvial discharge of those radionuclides, and ii) a methodology to estimate the discharge of those radionuclides. Secondly, studies in rivers and lakes in the vicinity of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant revealed the role of natural dissolved organics in affecting the dissolution and transport of 239,240Pu, 241Am through complexation to form soluble species with the aid of a chemical equilibrium model The same sort of a model was also applied successfully for the behavior of iron and manganese (hydr)oxides in river recharged aquifers which could bear riverborne radionuclides.